What is the history of AI?
A quick look at the growing technology's history, how it is impacting human life and what is coming in the future
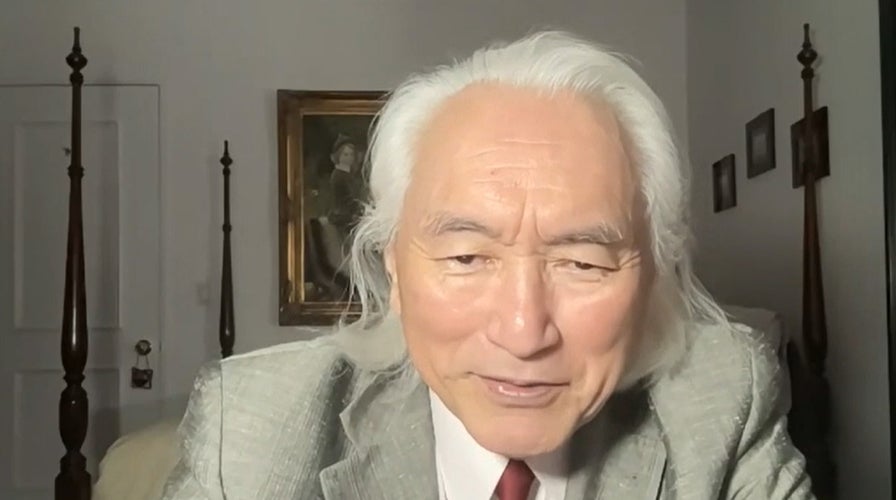
Dr. Michio Kaku, theoretical physicist, on the history of artificial intelligence
Dr. Michio Kaku discusses the advancements of AI since the early stages of development dating all the way back to Greek mythology and Pandora's box.
With the rapid emergence of artificial intelligence, which is quickly making its way into the daily lives of individuals around the world, there are a lot of questions circulating about the new technology.
Artificial intelligence has existed for a long time, but its capacity to emulate human intelligence and the tasks that it is able to perform have many worried about what the future of this technology will bring.

There are numerous questions about artificial intelligence, especially with the emergence of AI chatbots like ChatGPT. (iStock)
- Who invented artificial intelligence?
- What companies are developing AI?
- How does artificial intelligence work?
- What was the foundation of AI?
- What does the future of AI hold?
- How has AI changed the world?
- What are some key AI events in history?
- Who is the "Father of AI?"
- What were some major setbacks in AI?
1. Who invented artificial intelligence?
Though many can be credited with the production of AI today, the technology actually dates back further than one might think. Artificial intelligence has gone through three basic evolutionary stages, according to theoretical physicist Dr. Michio Kaku, and the first dates way back to Greek mythology.
"Stage one goes back to the Greeks, in fact, the God Vulcan, the God of the underworld, actually had robots," Dr. Kaku told Fox News Digital. "Even Leonardo da Vinci, the great painter, was interested in AI, and actually he built a robot. He actually built a robot out of gears, levers and pulleys."
Then, a second stage of AI took form, but not without its roadblocks.
Alan Turing, a British logician, computer scientist and mathematician made major contributions to AI before his death in 1954. He invented the Turing Machine, which implements computer algorithms, and wrote the scholarly paper, "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem", which paved the way for the function of modern computers.
In 1956, scientists gathered together at the Dartmouth conference to discuss what the next few years of artificial intelligence would look like.
"They thought we would have robots in just a few years," Dr. Kaku said. While that theory didn't hold true, it was not the end of AI, rather just one of the many bumps in the road that would continue in the years to come."
"It's had its ups and downs, ups and downs. Up, when people think that a new invention is going to change everything, and down when we realize how difficult it is, and how sophisticated the human brain really is," Dr. Kaku noted.
Then, the third stage of AI developed into digital computers and quantum computers, a technology that could completely revolutionize AI.
2. Which companies are developing AI?
There are a number of players participating in the advancements of AI. Many companies are widely using artificial intelligence as they conduct business and compete across the globe.
WHAT ARE THE DANGERS OF AI? FIND OUT WHY PEOPLE ARE AFRAID OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE

ChatGPT is an AI chatbot that was created by the company OpenAI. (LIONEL BONAVENTURE/AFP via Getty Images)
One of the companies to make a splash recently is OpenAI, which has partnered with Microsoft. OpenAI launched chatbot, ChatGPT, in 2022.
ChatGPT has become one of the most talked about AI systems in recent history. It is "trained to follow an instruction prompt and provide a detailed response," according to the OpenAI website. When operating ChatGPT, a user can type whatever they want into the system, and they will get an AI-generated response in return.
ChatGPT has raised public concern, prompting some AI leaders like Elon Musk to call for ethical guidelines with respect to AI regulation.
OpenAI's ChatGPT has dominated the AI conversation of late, but many other companies are exploring, developing and investing in the technology.
Chatbots like ChatGPT work by taking pieces of the internet and splicing them together, according to Dr. Kaku. He believes chatbots are here to stay, although they do have their problems, like not knowing truth from falsehood.
"Chatbots do not know the difference between true and false, right and wrong. … Even a child knows some of the basics of morality. Chatbots simply splice together different aspects of the internet and pass it off as if it wrote it itself," Dr. Kaku explained.
AI like chatbots are likely to have large impacts on the future job market. Dr. Kaku spoke on the importance of regulation when it comes to this kind of technology.
"There has to be a disclaimer some place saying this thing was written by a chatbot," Dr. Kaku said.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ‘GODFATHER’ ON AI POSSIBLY WIPING OUT HUMANITY: ‘IT’S NOT INCONCEIVABLE'
Google recently launched its own chatbot AI system called Bard. Adobe also offers AI products, including Sensei, which is billed to "bring the power of AI and machine learning to experiences" and Firefly, which employs generative AI technology.
Amazon also uses AI. If you have ever used Amazon, you are accustomed to seeing product recommendations. This is one way the company uses AI, by figuring out what kind of products you may be interested in purchasing based on your previous search and purchase history. Amazon also has its AI assistant Alexa hooked up to all its Echo devices. You can ask Alexa any question you like, and the system will give you an answer.
Apple offers the AI software Siri, which works similarly to Alexa. AI is also used in Apple Maps and with its face identification capabilities.
Baidu is a Chinese company, and is a competitor to Google. The platform has developed voice cloning technology which is regarded as highly authentic, prompting concerns of deepfakes. In 2018, its research arm claimed the ability to clone a human voice in three seconds.
IF AI ‘SPINS OUT OF CONTROL,’ WILL THE BOTS REFELCT VALUES FROM CHINA OR THE US?

Tesla vehicles are an example of artificial intelligence in practice although the company's founder, Elon Musk, has spoken out about the need to regulate AI. (Jeremy Moeller/Getty Images)
IBM is another AI pioneer, offering a computer system that can compete in strategy games against humans, or even participate in debates. JD.com, the Chinese e-commerce giant, has also made large investments in AI. Company founder Richard Liu has embarked on an ambitious path to be 100% automated in the future, according to Forbes.
Another commonly known company with strong artificial intelligence roots is Tesla, the electric vehicle company founded by Musk that uses AI in its vehicles to assist in performing a variety of tasks like automated driving.
3. How does artificial intelligence work?
An analysis of how artificial intelligence functions is difficult due to its extreme complexity.
At its core, AI is "the use of mechanical means to duplicate human behavior and thought," according to Dr. Kaku.

Amazon's Alexa, which is found on many of the company's devices, like the Echo, is an example of AI at work. (iStock)
AI EXPERT WARNS OF TOO MUCH ‘HYPE’: HUMANS WILL STILL BE IN CHARGE, WON'T BE ‘PETS’ TO NEW TECH
The way in which robots have been programmed over the course of the evolution of AI has changed. After the Dartmouth Conference, AI was largely based on coding. At the time, people believed that writing codes were going to create complex robots.
The advanced computers that were made using codes at the time were not very effective. The method used here was the "top-down" approach.
"The top-down approach is codifying all the laws of logic, all the laws of nature, in one gigantic code on a CD-ROM and inserting it into your robot and then the robot says ‘I think. I am aware. I exist. I’m alive.' That's the dream, putting everything on a disc, inserting it into a robot and the robot says, I'm alive."
This led to the introduction of the "bottom-up approach," which has more to do with learning from Mother Nature. In other words, teaching robots as if they were babies, so they can learn on their own, according to Dr. Kaku.
As a whole, there are four main types of artificial intelligence: reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind and self-awareness, according to Govtech.com.
There are four main types of AI, reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind and self-awareness. (iStock)
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT AI
Reactive machines refer to the most basic kind of artificial intelligence in comparison to others. This type of AI is unable to form any memories on its own or learn from experience.
Limited memory artificial intelligence, unlike reactive machines, is able to look into the past. A common example of a limited memory artificial machine is a self-driving car.
Theory of mind AI involves very complex machines that are still being researched today, but are likely to form the basis for future AI technology. These machines will be able to understand people, and develop and create complex ideas about the world and the people in it, producing their own original thoughts.
Finally, the last frontier in AI technology revolves around machines possessing self-awareness. While leading experts agree that technology such as chatbots still lacks self-awareness, the skill at which they engage in mimicry of humans, has led some to suggest that we may have to redefine the concepts of self-awareness and sentience.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE QUIZ! HOW WELL DO YOU KNOW AI?
4. What was the foundation of AI?
Philosophy, mathematics, economics, neuroscience, psychology, computer engineering and linguistics have all been disciplines involved in the development of AI.
Scientists and researchers involved in these fields developed the most basic form of artificial intelligence: reactive machines. Reactive machines are the foundation of more complex AI.
This AI base has allowed for more advanced technology to be created, like limited memory machines.
5. What does the future of AI hold?
In the future, we may envision fully self-driving cars, immersive movie experiences, robots with advanced abilities, and AI in the medical field. The applications of AI are wide-ranging and are certain to have a profound impact on society.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
AI has already advanced so rapidly that it is hard to predict what will happen just a few years from now. What is likely to happen is that AI will make its way into pretty much every part of our lives and every facet of our economy in some fashion.
AI could be used more in healthcare to do things like make diagnoses and help doctors make decisions about a patient's care.
AI may also be used more to perform simple everyday tasks, like assist with household chores.
Self-driving cars will likely become widespread, and AI will play a large role in manufacturing, assisting humans with mechanisms like robotic arms.
Even the entertainment industry is likely to be impacted by AI, completely changing the way that films are created and watched.

Artificial intelligence will continue to change the world in the future. (Rafael Henrique/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
In the future, quantum computing is going to drastically change AI, according to Dr. Kaku.
"We're going to the next era. We're leaving the era of digital that is computing on zeros and ones, zeros and ones, and computing on molecules, computing on atoms, because that's the language of Mother Nature," Dr. Kaku explained.
"One day, quantum computers will replace ordinary computers. … Mother Nature does not use zeros and ones, zeros and ones. Mother Nature is not digital, Mother Nature is quantum."
Today, quantum computers are in their beginning stages, but it is not a completely futuristic idea.
"Now at the present time, of course, we have operating quantum computers, they exist. This is not science fiction, but they're still primitive," Dr. Kaku said.
The creation of a quantum computer is costly and complex, but Dr. Kaku believes that one day, the technology will be in our hands.
The jobs of the future are also going to see major changes because of AI, according to Dr. Kaku. He advises people should start learning about the technology for future job security.
When it comes to chatbots in particular, even though they have their problems, jobs in the future are expected to see AI incorporated into workflow.
"In the future, the jobs will be going to those people who know how to use a chatbot. This is going to save tremendous amounts of effort, save time, save money. They're here to stay, but you have to realize the limitations of this technology too," Dr. Kaku said.
The jobs that are most vulnerable in the future, according to Dr. Kaku, are the ones that are heavily based on repetitive tasks and jobs that include doing a lot of search.
On the other hand, blue collar work, jobs that involve a lot of human interaction and strategic planning positions are roles that robots will take longer to adapt to. Jobs that require great creativity and thinking are roles that robots cannot perform well.
Jobs are ever-changing, and AI is no different. For example, while an X-ray scan can be done by AI in the future, there's going to need to be a human there to make those final decisions, Dr. Kaku said. Those who understand AI and are able to use it are those who will have many job opportunities in the future.
"You have to retrain yourself and adapt yourself to the new technology, because that is inevitable," Dr. Kaku said.
6. How has AI changed the world?
AI has changed a lot of fundamental aspects of day to day life, especially when it comes to work and the ways we communicate with one another.
AI has made a number of tasks easier for humans, like being able to use a GPS on our phones to get from point A to point B instead using a paper map to get directions. The more advanced AI that is being introduced today is changing the jobs that people have, how we get questions answered and how we are communicating.
Jobs have already been affected by AI and more will be added to that list in the future. A lot of automated work that humans have done in the past is now being done by AI as well as customer service-related inquiries being answered by robots rather than by humans. There are also different types of AI software being used in tech industries as well as in healthcare.
WHO IS WATCHING YOU? AI CAN STALK UNSUSPECTING VICTIMS WITH ‘EASE AND PRECISION’: EXPERTS

Snapchat's My AI feature is one example of an AI chatbot. (Muhammed Enes Yildirim / Anadolu Agency via Getty Images)
AI has changed the way people learn, with software that takes notes and write essays for you, and has changed the way we find answers to questions. There is very little time spent going through a book to find the answer to a question, because answers can be found with a quick Google search. Better yet, you can ask your phone a question and an answer will be verbally read out to you. You can also ask software like ChatGPT or Google Bard practically anything and an answer will be quickly formatted for you.
With chatbots on the rise, AI has also changed the way we communicate with others. Now, you can have ongoing conversations with a bot and get an immediate response, like with Snapchat's My AI feature.
It has also changed the way we conduct daily tasks, like commutes with self-driving cars and the way we do daily chores with tools like robotic vacuum cleaners.
These are just a few ways AI has changed the world, and more changes will come in the near future as the technology expands.
7. What are some key AI events in history?
Though AI is discussed now more than ever, historically, there are numerous milestones worth noting.
- Alan Turing's model, the Turing Machine.
- Turing's scholarly paper titled "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem."
- John McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence" and created the LISP language for the IBM 704 computer in 1958.
- In the late 1990s, there was the creation of the robot pet dog, released by Sony.
- In 2011, IBM's Watson computer competed against past "Jeopardy" winners and won by large margins.
- In 2016, Google DeepMind's AlphaGo beat the Go world champion Lee Sedol.

IBM Watson AI technology was used to win "Jeopardy" in 2011. (Michael Nagle/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
8. Who is the "Father of AI?"
Although there are many who made contributions to the foundations of artificial intelligence, it is often McCarthy who is labeled as the "Father of AI."
McCarthy carries this title mainly because he was the one who initially coined the term "artificial intelligence" which is used today.
9. What were some major setbacks in AI?
The significant setbacks for AI are more recent as the technology has become both advanced and accessible to the public. This includes issues with bias, legal concerns and security.
AI is also challenging to explain to humans. It is so pervasive, with many different capabilities, that it has left many fearful for the future and uncertain about where the technology is headed.
Some major setbacks in reference to AI are currently left unresolved.
"Every technology is a double-edged sword. Every technology without exception," Dr. Kaku said. "We have to make sure that laws are passed, so that these new technologies are used to liberate people and reduce drudgery, increase efficiency, rather than to pit people against each other and hurt individuals."




